Regional and International Implications of the Operation
1. Turkey’s Role and Regional Policy
Turkey remains a key player in the region, with its military presence in Idlib and efforts to maintain de-escalation zones. While there is no confirmed direct involvement in the operation, the opposition’s advancements align with Turkey’s strategic interests. Ankara may leverage these developments as a pressure point against the Syrian regime, especially after stalled negotiations with Damascus. This could compel the regime to return to the diplomatic table.
Turkey’s primary focus is to prevent a potential wave of migration by keeping displaced populations within Syrian borders and establishing secure zones in Idlib. Consequently, Turkey’s diplomatic and military maneuvers are likely to maintain a delicate balance between humanitarian concerns and strategic interests.
2. Russia-Turkey Relations
The Serakib and Aleppo operations present a critical test for Russia-Turkey relations. As one of the guarantors of the Astana process, Russia is known to coordinate with the Syrian regime in Idlib. However, with its focus diverted to the war in Ukraine, Moscow may avoid escalating tensions with Turkey.
Russia’s limited intervention in the form of airstrikes can be interpreted as a balancing act. Still, its response to any expansion of the operations remains uncertain and could strain relations between Ankara and Moscow.
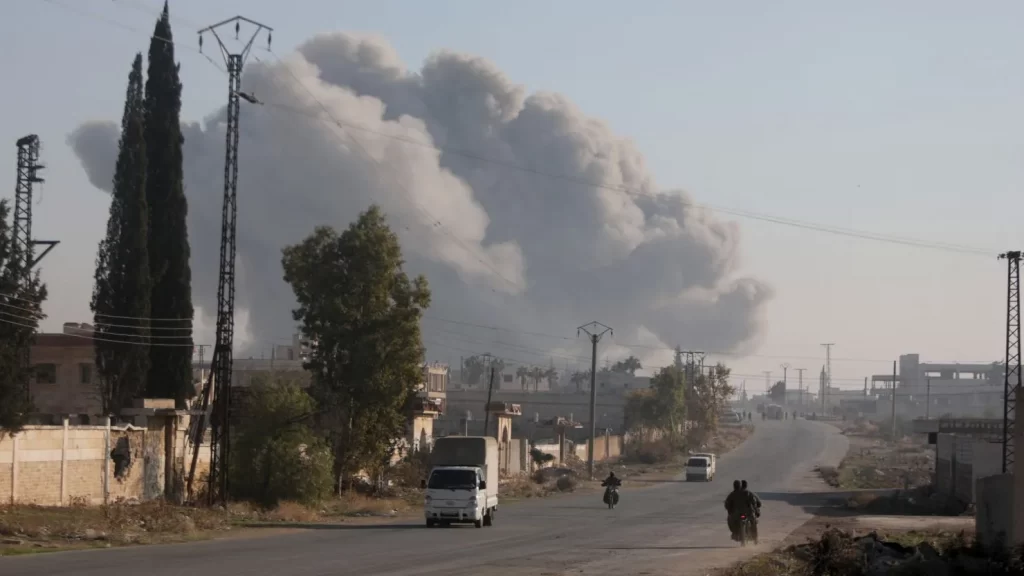

3. Iran’s Diminished Influence
The reduced impact of Iran-backed militias on the battlefield has become evident. The death of an Iranian military advisor and the retreat of Iranian-aligned forces during the Serakib operation highlight Tehran’s losses. This weakening influence creates new opportunities for other regional actors to reshape the dynamics in Syria.
4. The U.S. and the West’s Perspective
Western countries, including the U.S., tend to view developments in Idlib primarily through the lens of the humanitarian crisis. While the Serakib operation might draw renewed attention to Syria, it is unlikely to alter the U.S.’s low-priority approach to the conflict. Western responses are expected to focus on calls for humanitarian aid rather than direct intervention.
5. The Future of the Opposition and Internal Dynamics
This operation could serve as a unifying force for Syrian opposition groups, providing renewed motivation. However, achieving lasting success will depend on their ability to establish a unified command structure. Internal divisions and ideological differences among opposition factions could hinder their efforts to translate these gains into a sustainable long-term strategy.
6. Status of Ceasefire Agreements
The operation’s impact on the status of de-escalation zones outlined in the Astana process is significant. Violations or renegotiations of these agreements could be on the horizon. Keeping military activities within the boundaries of these zones may prevent a complete collapse of existing agreements between Turkey, Russia, and Iran.

Potential Scenarios
1. Opposition’s Strategic Goals
By gaining control of strategic locations like Serakib, the opposition seeks not only battlefield dominance but also a stronger position in political negotiations. Retaking areas lost in 2019-2020 holds both military and symbolic importance.
Key objectives include:
- Full control of the M5 and M4 highways, cutting off regime supply lines and securing logistical advantages.
- Strengthening positions near Aleppo to increase pressure on regime forces.
- Creating safe zones to encourage the return of refugees, thereby addressing both humanitarian and political goals.
2. Likely Responses from the Regime and Allies
The Syrian regime may attempt to recover lost ground through counterattacks, though its current capacity is limited due to logistical and manpower challenges. Iran-backed militias have weakened, and Russia’s reduced involvement has further isolated the regime.
Potential regime strategies include:
- Mobilizing local militias to regain control.
- Conducting intensive airstrikes despite limited resources.
- Using propaganda to undermine opposition unity and morale.
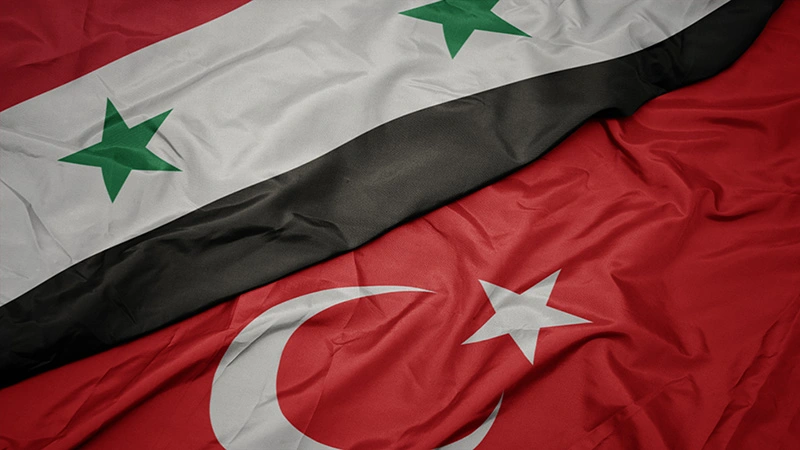

3. Implications for Turkey-Russia Relations
This period could test the resilience of the Astana process and existing agreements. Escalations might prompt renewed negotiations between Turkey, Russia, and Iran, aimed at preventing further destabilization. A new understanding between Ankara and Moscow could help manage the conflict’s broader implications.
Long-Term Prospects
Maintaining control over Serakib could shift the balance of power in the Syrian civil war. However, this progress is fraught with risks:
- The regime’s potential to launch a major counteroffensive if given the opportunity.
- Renewed engagement from Russia and Iran, escalating the conflict.
- Internal rivalries among opposition factions, threatening the sustainability of their gains.
Russia’s Strategic Calculations
Russia’s focus on Ukraine has limited its engagement in Syria, yet developments in Serakib may force Moscow to reassess its priorities:
- Limited but targeted military support to the regime to stall opposition progress.
- Seeking new agreements with Turkey to consolidate influence over both the regime and opposition.
- Leveraging the situation in diplomatic negotiations with Western powers and Turkey.
Role of the International Community
The capture of Serakib could revive global interest in Syria, though responses may vary in intensity:
- The European Union may enhance cooperation with Turkey to mitigate a potential migration crisis and allocate more humanitarian aid.
- The U.S. is likely to maintain its low-priority stance, with limited engagement focused on addressing humanitarian concerns.
- Gulf countries might increase support for opposition forces, further diminishing Iran’s regional clout.